Polylactic Acid Films
Properties
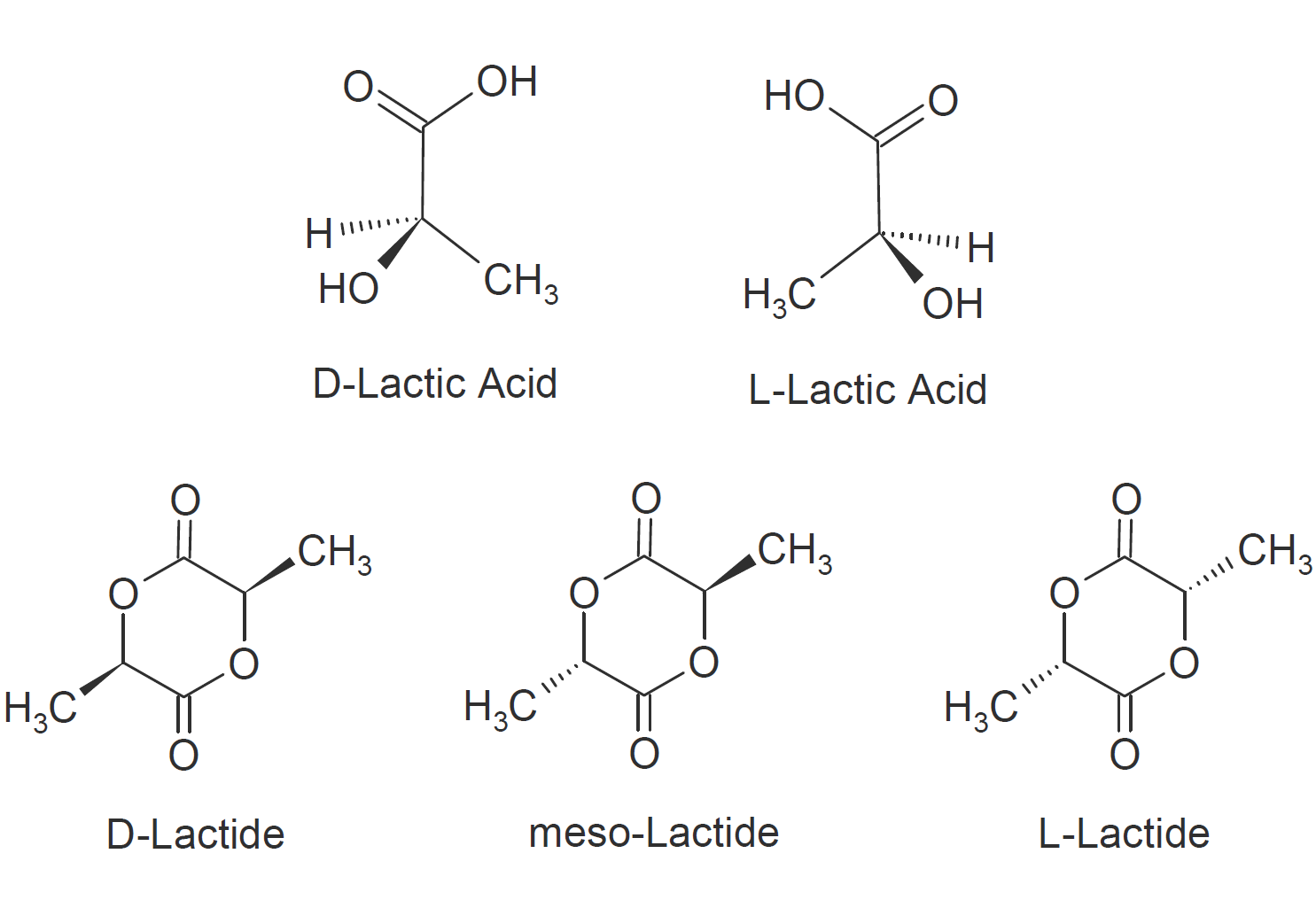
Poly(lactic acid) or polylactide (PLA) is a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources such as corn starch, tapioca or sugar cane. The fermentation of starch (dextrose) yields two optically active enantiomers, namely D (-) and L (+) lactic acid. Polymerization is carried out by either direct condensation of the lactic acid monomers or by ring-opening polymerization of the cyclic diesters (lactides). The resulting resins can be easily converted into films and sheets via standard forming methods including injection and blow molding.
The properties of PLA like melting point, mechanical strength, and crystallinity depend on the proportions of the D(+) and L(-) stereoisomers in the polymer and on the molecular weight. As for other plastics, the properties of PLA films will also depend on compounding and on the manufacturing process.
Typical commercial grades are amorphous or semi-crystalline and have very good clarity and gloss and little to no odor. Films made of PLA have very high moisture vapor transmission, and very low oxygen and CO2 transmission rates. PLA films also have good chemical resistance to hydrocarbons, vegetable oils, and the like but are not resistant to polar solvents such as acetone, acetic acid and ethyl acetate.
The mechanical properties of PLA films are greatly affected by its composition and the processing conditions, that is, whether or not it is annealed or oriented and what its degree of crystallinity is. It can be formulated and processed to be flexible or rigid, and can be copolymerized with other monomers to further modify its properties.The tensile strength and elastic modulus can be similar to those of PET.1 However, typical PLA grades have a lower maximum continuous service temperature. Often plasticizers are added which (greatly) improve its flexibility, tear resistance and impact strength (pure PLA is rather brittle). Some novel grades also have much improved heat stability and can withstand temperatures up to 120°C (HDT, 0.45MPa).2 However, typical grades have a relative low heat deflection temperature in the range of 50 - 60°C. The heat performance of general purpose PLA is typically between LDPE and HDPE and its impact strength is comparable to HIPS and PP whereas impact modified grades have much higher impact strength comparable to ABS.
Most commercial PLA films are 100 percent biodegradable and compostable. However, the biodegradation time can vary greatly depending on composition, crystallinity and environmental conditions.
Applications
PLA is mainly used in the packaging industry for cups, bowls, bottles and
straws. Other applications include disposable bags and trash liners
as well as compostable agriculture films.
PLA is also an excellent
choice for biomedical and pharmaceutical applications such as drug delivery systems
and sutures because PLA is biodegradable, hydrolysable and generally recognized as safe.4